Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) is an important thermal characteristic that allows manufacturers to evaluate how plastics perform when they are used at elevated temperatures while under load. For example, engineers, manufacturers, and professionals associated with quality can determine whether a particular grade of plastic will retain shape and strength under heat and stress when it is being utilized in actual service conditions.
What is Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) is the temperature at which a material begins to deform under a specified load as heat is applied. Also known as Deflection Temperature Under Load (DTUL), it indicates a plastic’s ability to resist bending and maintain shape at elevated temperatures.
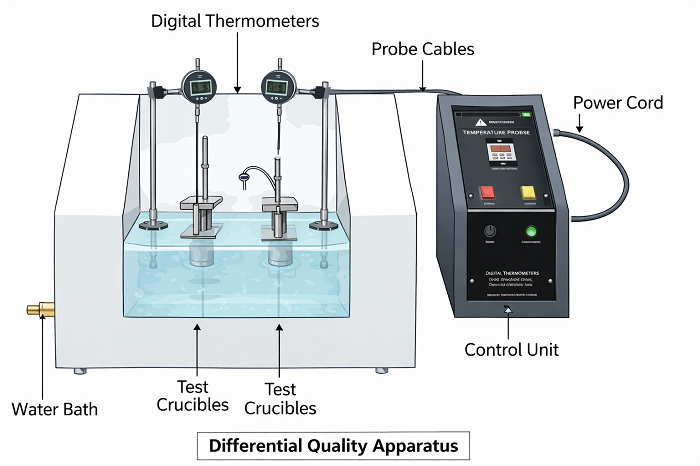
The heat-deflection temperature (HDT) is the point at which a specimen of plastic will bend by 0.25 mm when a specific amount of weight is applied to it. HDT values represent the major types of plastic performance testing conducted on plastics that use heat to provide testing.
Why Heat Deflection Temperature is Important for Plastics
Heat Deflection Temperature guides are used to identify the failure temperature of materials used in structural applications. Using the Heat Deflection Temperature of the same material can compare the relative performance of materials against each other. In addition, the HDT will indicate the relative performance of a molded plastic component with respect to heat and mechanical load conditions.
Formula for Heat Deflection Temperature
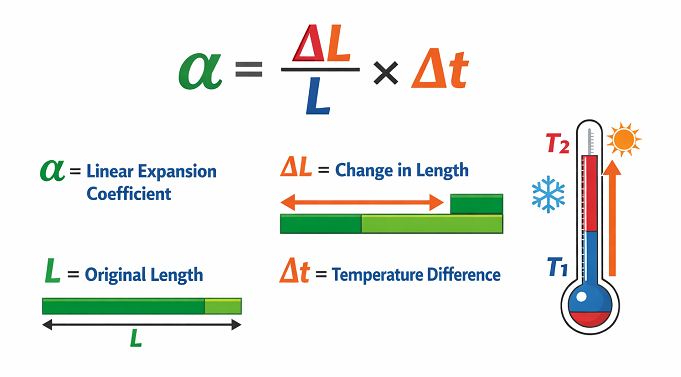
Through exposure to heat or cold, thermal deformation is the expansion and contraction of a material (or fabric) as a result of temperature changes (thermal). The code in which thermal deformation is manifested is referred to as the linear expansion coefficient, denoted as α, and it is defined as:
α=ΔL/L×Δt
Where:
α = Linear expansion coefficient of a substance.
ΔL = Expansion or contraction value of a specimen.
L = Length before heating or cooling.
Δt = The temperature difference
How Heat Deflection Temperature is Measured
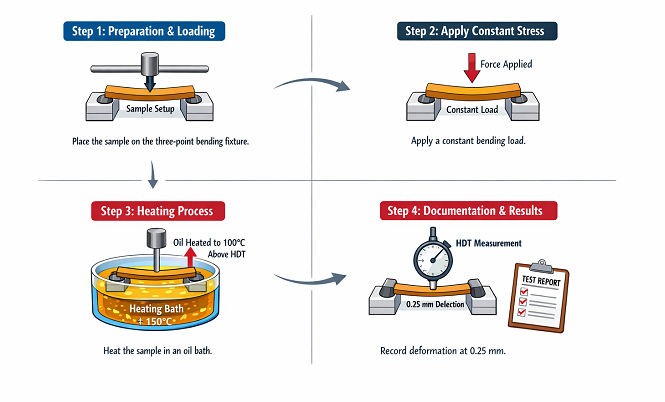
To determine a material's Heat Deflection Temperature, heating, load, and measurement systems must be used, all of which are available in the testing equipment. The test method used to measure HDT is ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) D648, which is similar in method to ISO 75 (International Organization for Standardization).
The Heat Deflection Temperature measuring process consists of the following 4 steps:
Step 1: Preparation and Loading Your Sample
Your sample should be arranged and set up on the designated machine using a three-point flexural (bending) support (the end supports hold the main portion of the body straight while a force is applied to the center).
Step 2: Apply Constant Bending Stress
The same constant bending stress should be applied to the center of the sample throughout the testing. To determine a constant bending stress measurement based on the material that you are testing:
Step 3: Heating Process
The heating process must use either a mineral oil or silicone oil to keep the samples and their properties stable through the temperature rise due to flex. There are some differences in how they are heated; however, you need to heat them to a temperature of around 100°C above the HDT temperature as you proceed with the test to obtain a reading.
Step 4: Documentation and Results
Keep records of all stages, temperatures, and HDT readings of your sample during the test until the sample deforms 0.25 mm in accordance with International standards.
Heat deflection temperature vs glass transition temperature
Here is the difference between Heat Deflection Temperature and glass transition temperature:
|
Basis of Comparison |
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) |
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) |
|
Definition |
The temperature at which a plastic deforms under a specified load |
The temperature at which a polymer changes from a rigid, glassy state to a rubbery state |
|
Type of Property |
Mechanical and thermal performance property |
Thermal and molecular properties |
|
Measured Under Load |
Yes, measured under a fixed mechanical stress |
No, measured without applying an external load |
|
Physical Change |
Indicates the onset of visible deformation |
Indicates a change in molecular mobility |
|
Applies To |
Thermoplastics and some thermosets |
Mainly thermoplastics and amorphous polymers |
|
Testing Method |
Three-point bending test under controlled load |
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) or Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) |
|
Practical Use |
Determines maximum service temperature under load |
Determines the temperature range for stiffness and flexibility |
|
Standards |
ASTM D648, ISO 75 |
ASTM E1356, ISO 11357 |
Common HDT Values for Different Types of Plastics
Here are the common HDT Values for different types of plastics:
|
Polymer Name |
HDT @ 0.46 MPa (Min–Max °C) |
HDT @ 1.8 MPa (Min–Max °C) |
|
ABS – Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
68 – 100 |
88 – 100 |
|
ABS Flame Retardant |
90 – 120 |
80 – 110 |
|
ABS High Heat |
100 – 125 |
85 – 120 |
|
ABS High Impact |
90 – 110 |
80 – 100 |
|
ABS/PC Blend |
105 – 130 |
100 – 110 |
|
ABS/PC Blend (20% Glass Fiber) |
130 – 130 |
115 – 115 |
|
ABS/PC Flame Retardant |
90 – 110 |
80 – 110 |
|
Amorphous TPI Blend (Ultra-high heat, High Flow) |
263 – 263 |
240 – 240 |
|
Amorphous TPI Blend (Ultra-high heat, Standard Flow) |
260 – 260 |
238 – 238 |
|
Amorphous TPI, High Heat, 30% Glass Fiber |
257 – 257 |
254 – 254 |
Heat Deflection Temperature Standards
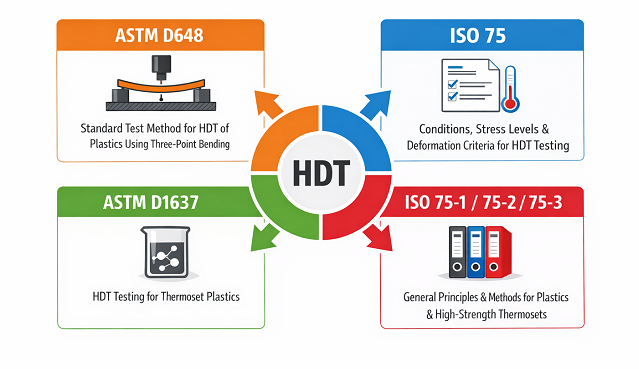
The standard for measuring Heat Deflection Temperature consists of four different organizations. ASTM D648, ISO 75, ASTM D1637, and ISO 75. Each of these organizations provides information on how to perform the measurement as well as test procedures.
-
ASTM D648: Provides the standardised method for determining the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of plastic materials, based on controlled loads by the method of three-point bending tests.
-
ISO 75: Defines the different conditions under which a test to determine HDT can be conducted and includes the amount of stress and how much of deformation that should occur to the material.
-
ASTM D1637: It is a standard for the measurement of HDT for thermoset plastic materials.
-
ISO 75-1 / 75-2 / 75-3: Describes the overall fundamentals, testing methods for plastics, and testing methods for extremely high-strength thermosets for evaluation of their HDT.
Conclusion
Both thermal and mechanical properties of plastics are tested by means of the Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT). Knowledge of the HDT, the techniques used to determine it, and the standards that exist in different forms of HDT would enable plastic manufacturers and designers to select the correct plastic to use in an application where it has to be resistant to heat. This makes sure that the plastic products will possess the durability, safety, and the best-performing nature when they are exposed to real-life uses.





