Humidity testing is conducted in different industries to check the way a product will respond when it is in the presence of various amounts of humidity in the immediate environment. A humidity test is done by placing the product under test in a controlled humidity environment and evaluating its performance and durability, as well as long-term stability.
The purpose of this kind of testing is to make sure that products and materials can work in the correct and safe way in the conditions where moisture can lead to such unwanted effects (degradation, corrosion, or failure).
Importance of Humidity Testing in Laboratories?
- Laboratories rely on humidity testing for various reasons. First, it ensures product reliability. Researchers use either high or low humidity levels to expose any weaknesses in the material being tested by looking for possible places where the material could fail within an electrical device, such as through moisture causing short circuiting and corrosion of the insulation around wires and electrical connections and proper connection of the electrical components of the electronic device.
- Humidity testing also aids in quality control. Humidity testing gives manufacturers information as to whether or not products are within the set humidity tolerance limits. As an illustration, pharmaceuticals need to ensure that the required level of humidity is maintained to be effective; when the product contains more water than the acceptable level of moisture, then its chemical stability will be altered.
- The third kind of testing, which the majority of the laboratories carry out, is the humidity testing to simulate the environmental conditions during the production of a product. The climate of most products goes through numerous forms of extreme climate conditions during their lifetime, such as very hot and humid climate conditions in the tropical areas and very cold and dry climatic conditions during the winter seasons.
Different Methods of Humidity Testing
A variety of measurement methods are used to perform humidity testing utilizing psychrometric, hygrometric, electronic sensors, dew point, and gravimetric as their basis.
Each method has different levels of accuracy for the specific use of environmental chambers, as well as the many industries that require humidity measurement.
-
Psychrometric (Wet-Dry Bulb)
The comparison between wet and dry bulb temperatures provides an indirect method of measuring humidity using evaporative cooling. This method is used regularly, but its accuracy depends upon the amount of air moving over the wet wick and also upon the purity of the water being used.
-
Hygrometric (Mechanical)
This method utilizes the expansion and contraction of human hair or synthetic material (usually synthetic) within a dial constructed out of these two types of materials. It is simple and visual but does not provide a specific measurement of the humidity.
-
Electronic Sensors
Humidity levels can be measured with electronic sensors via a variety of methods as follows: capacitive—the amount of moisture absorbed by a material results in an increase in capacitance; resistive—a material's resistance to the flow of electricity will change with added moisture; thermal conductivity—the thermal properties of air, which relate to the amount of water vapor contained in it, can be measured with thermal conductivity sensors.
-
Dew Point
It provides high accuracy for critical applications, including meteorology, industrial processes, HVAC systems, and laboratory testing at the point of condensation of water vapor on a cooled surface, to allow for precise control of moisture-sensitive materials and environments.
-
Gravimetric (Sorption)
It is a technique that measures the mass change (either gain or loss) of hygroscopic materials as they take in moisture and is used as a highly precise reference standard for solid materials, including food items, soil, pharmaceuticals, and polymers. It is required to perform further research, maintain high-quality control standards, and conduct stability analysis on these materials.
Applications of Humidity Testing
Humidity testing provides various applications across several industries, such as electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, textiles, and construction materials. Here are the applications described in detail:
Electronics
Humidity testing in electronics determines how much humidity can cause corrosion, shorts, or burns and will help determine if a product is reliable and safe and can withstand extreme environmental conditions such as those encountered in a humid tropical environment.
Automotive Industry
Automotive humidity testing examines automotive components, including dashboard assemblies, sensor assemblies, wiring harnesses, and other plastic components, for failure due to cracking, fading, corrosion, or reduced functionality. Automobile humidity testing is performed to ensure vehicles remain capable of operation under the influence of environmental factors.
Pharmaceuticals
Humidity tests in the pharmaceutical industry assure stability and prevent drugs from degrading due to moisture but also test the integrity of the packaging. Controlled humidity testing ensures the continued effectiveness, safety, and shelf life of medicines, vaccines, and medical devices, particularly in tropical regions as well as when stored for long periods of time.
Food & Beverage
Humidity levels are utilized by food and beverage manufacturers to identify the performance capabilities of their packaging, moisture absorption rates, and product shelf life. Excess moisture in the packaged product can lead to spoilage/clumping and bacterial growth. Thus, testing humidity levels helps ensure food safety/quality and compliance with government regulations during storage, transport, and distribution.
Textiles
The fact of the garment, fiber, and fabric humidity can be tested to determine the risk of mold growth, color loss, shrinking, and the alteration of such features as elasticity and more. This can have an impact on the life, quality, and usage of the textile when it is stored or used.
Construction Materials
Moisture resistance, cracking, mold growth, and structural integrity of building materials when used in construction are checked through humidity testing. Besides these areas of concern, the durability, longevity, and performance of these same materials may be identified by carrying out humidity testing.
Standards Used in Humidity Testing
The humidity test standards are determined by the standards established by different bodies like IEC, ASTM, and ISO. Some of the common humidity tests are IEC 60068-2-78 (electronic), MIL-STD-810G method 507.5 (military/rugged), ASTM D1776/D2247 (textiles, coatings), and ISO 6270-2 (paints, varnishes).
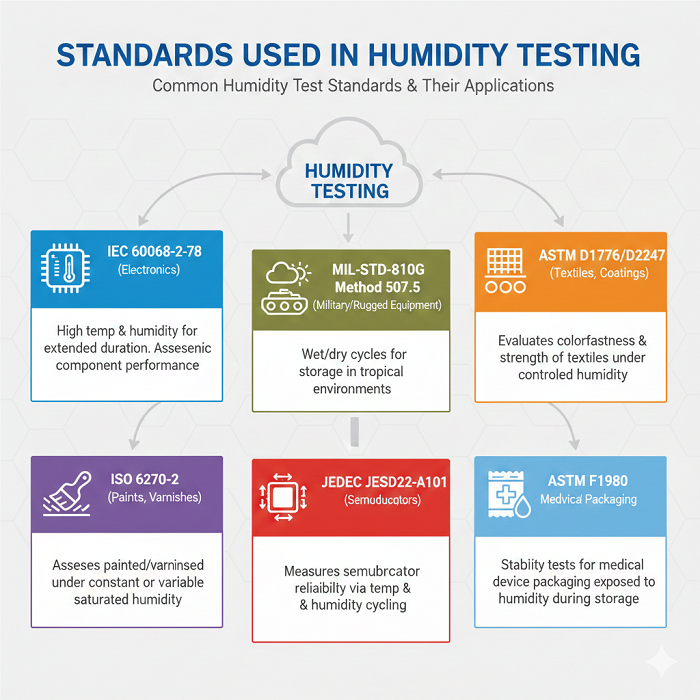
Here are the standards described:
-
IEC 60068-2-78: Tests are performed under a specified temperature that is significantly higher than room temperature and in humid conditions to ascertain the degree of performance of electronics and electronic components over an extended duration; the greatest extent of relative humidity level is specified in IEC 60068-2-78.
-
MIL-STD-810G Method 507.5: Method 507.5, like IEC 60068-2-78, is intended to test the ability of industrial military equipment to survive the wetting and drying cycle that may occur in practice during the storage of equipment in a tropical environment or during storage under tropical conditions.
-
ASTM D1776/D2247: Test to complete the experiment, which aims at identifying whether the properties of the textile or textile-coated materials, such as colorfastness and strength, are influenced in the presence of a controlled level of humidity during storage or use.
-
ISO 6270-2: Like the MIL-STD-810G, ISO 6270-2 has procedures to ascertain whether the painted surface or a varnished surface is subjected to constant or variable exposure to saturated humidity.
-
JEDEC JESD22-A101: The JESD22-A101 test procedure is largely aimed at measuring the semiconductor reliability by checking how the semiconductors will behave regarding cycling of temperature and humidity.
-
ASTM F1980: ASTM F1980 describes the stability tests done on packaging used for medical devices when exposed to humidity during storage and use.
Testronix Humidity Test Chamber: Best Equipment for Humidity Testing
Testronix Instruments offers modern humidity test chambers designed to simulate the exact conditions of humidity and temperature in which the lab tests should be conducted. The advantage of these chambers lies in accelerated aging tests and environmental simulation, as they have uniform distribution of humidity, accurate control, and programmable test cycles. The robust design and easy user interfaces of Testronix chambers enable the laboratories to successfully carry out high-accuracy testing of humidity.
What stands out Testronix is that it enables users to reproduce a range of climatic conditions, from dry weather to tropical humidity, with scalable testing parameters. The multi-layered digital control system guarantees that there is precision in the monitoring and recording of the data which is crucial in quality assurance, research, and meeting the international standards.
Conclusion
A humidity test is an important process in modern laboratories that ensures reliability, consistency, and longevity of products in any number of industries. The knowledge of the behavior of materials in the presence of moisture is vital in quality control and the safety of products in many sectors, such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and textiles. Testing methods, which include advanced humidity chambers and salt solutions, are flexible and precise in monitoring the environmental effects.