Corrosion testing is an essential method to analyze the performance and durability of materials, particularly metals and coated surfaces, in extreme conditions. Industries like automotive, aerospace, marine, and construction require trustworthy methods of testing to ascertain that the products can perform under actual environmental conditions. Of all the accelerated corrosion test methods, the Salt Spray Test (SST) and the Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) are among the most common.
Both SST and CCT are intended to forecast the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings, but they vary greatly in methodology, precision, and usage. While the salt spray test is commonly known as a fast, standardized, and low-cost test method, the cyclic corrosion test is more sophisticated, mimicking natural environmental fluctuations for precise field performance. This blog discusses the two approaches in depth, how they work, their differences, similar standards, and why selecting a test that works is important.
What is Salt Spray Test (SST)
The Salt Spray test (SST), also referred to as a Salt Fog Test, is an accelerated corrosion test to determine the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. Manufacturers can estimate the longevity and sturdiness of their products in corrosive conditions, including marine and road-salt conditions, by exposing samples to a controlled, high-concentration salt-water mist.
Working Process of the Salt Spray Test:
-
Sample preparation: Test samples, which may be metal components, coated panels, or fasteners, are cleaned and placed within the test chamber. They are usually mounted at a 15- to 30-degree angle from the vertical so that the salt mist is able to strike all surfaces.
-
Salt solution blend: A definite salt solution is made to standard industry practice. The most widely used is 5% sodium chloride (NaCl) solution blended with deionized water, the pH of which is carefully maintained between 6.5 and 7.2.
-
Fog production: Wet, humidified, and heated air is forced through a nozzle to atomize saltwater solution, producing a heavy salt fog that occupies the chamber.
-
Controlled environment: The chamber has a constant temperature, usually 35°C (95°F), during the test. Such an environment, comprising continuous, wet, and high-chloride conditions, intensely accelerates corrosion.
-
Test duration: Samples are subjected to the corrosive fog for a specific time period, which may range from 24 hours to weeks, based on the material and industry regulations.
-
Evaluation: Following the test, the specimens are withdrawn and examined for evidence of corrosion, including red rust (on steel), white rust (on zinc coating), blistering, or other damage to the coating. The results are compared against pre-determined pass/fail standards to ascertain the effectiveness of the coating.

What is Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT)
A Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) is a sophisticated laboratory test that mimics and accelerates the influence of actual environmental corrosion on coatings and materials.
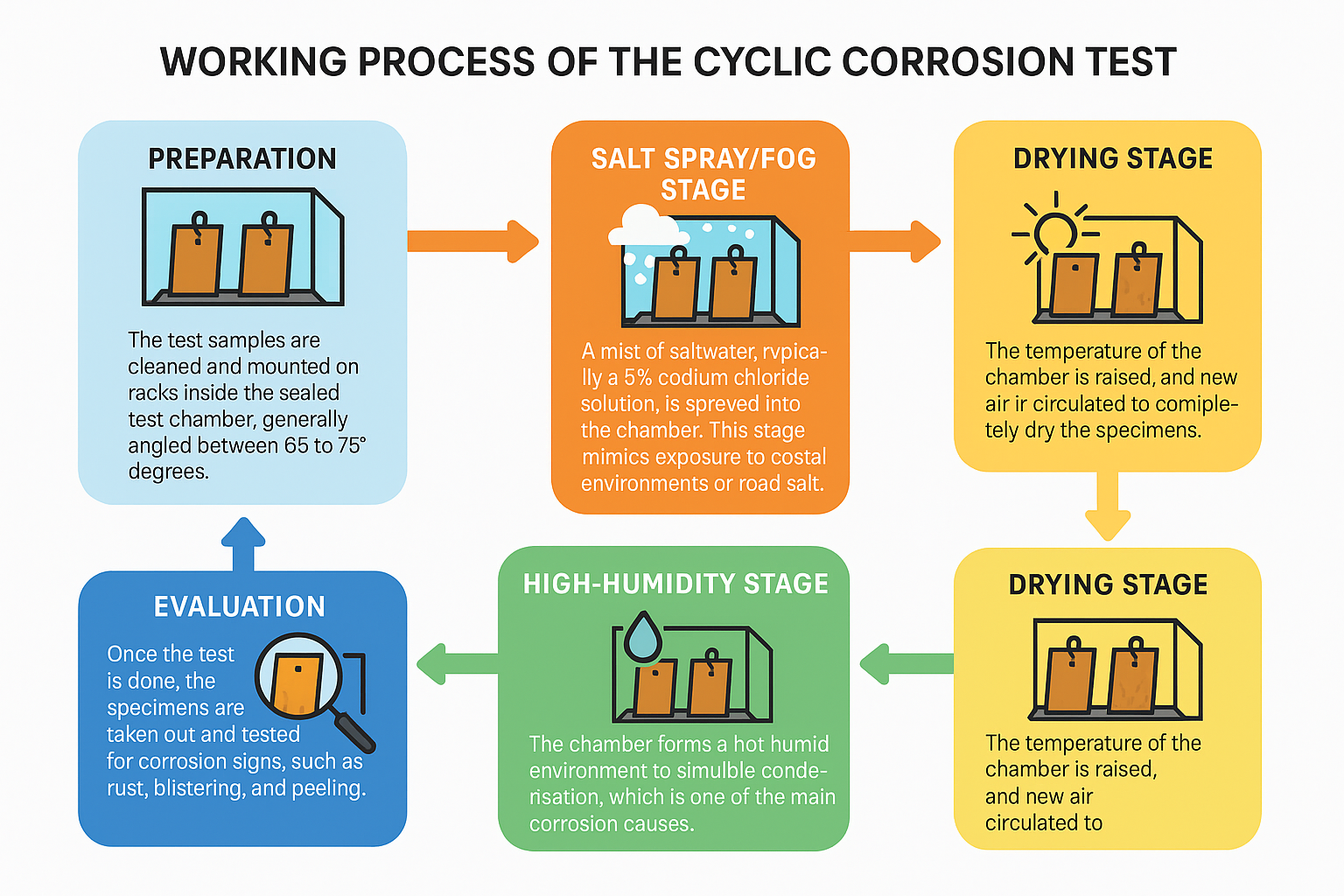
Working Process of the Cyclic Corrosion Test:
-
Preparation: The test samples are cleaned and mounted on racks inside the sealed test chamber, generally angled between 65 to 75 degrees.
-
Salt Spray/fog Stage: A mist of saltwater, typically a 5% sodium chloride solution, is sprayed into the chamber. This stage mimics exposure to coastal exposures or road salt.
-
Drying Stage: The temperature of the chamber is raised, and new air is circulated to completely dry the specimens. This mimics outdoor drying and eliminates repeated surface wetness, more representative of continuous salt spray tests.
-
High-humidity Stage: The chamber forms a hot, humid environment to simulate condensation, which is one of the main corrosion causes. A cooling stage is incorporated in some protocols in order to further this effect.
-
Cycle Repetition: The chamber repeats the given cycle of wet, dry, and humid stages automatically for the test period.
-
Evaluation: Once the test is done, the specimens are taken out and tested for corrosion signs, such as rust, blistering, and peeling. Results assist manufacturers in evaluating material performance and making product design better.
Difference Between Salt Spray Test (SST) and Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT)
The main difference between a Salt Spray Test (SST) and a Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) is that SST exposes a sample to constant saline fog, while CCT alternates environments like salt spray, humidity, and drying. Since a CCT more closely approximates the alternating wetting and drying of an outdoor atmosphere, it gives a more accurate and trustworthy forecast of a material's actual corrosion resistance than an SST.
SST vs CCT Testing
|
Parameters |
Salt Spray Test (SST) |
Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) |
|
Purpose |
Quick evaluation of corrosion resistance |
Realistic simulation of environmental corrosion |
|
Working Principle |
Continuous exposure to salt fog |
Alternating cycles of salt spray, humidity, drying, and temperature changes |
|
Test duration |
Typically, 24 to 1000+ hours |
A few days to several weeks, depending on cycles |
|
Environmental Simulation |
Constant marine-like environment |
Real-world weathering conditions |
|
Accuracy |
Limited correlation with outdoor performance |
High correlation with actual field performance |
|
Equipment Required |
Simple salt spray chamber |
Advanced programmable cyclic corrosion chamber |
|
Cost |
Low |
Higher |
|
Applications |
ASTM B117, ISO 9227 |
ISO 14993, VDA 233-102 |
Difference in Testing Methodologies
The Salt Spray Test (SST) is a continuous exposure test where samples are exposed in a constant salt fog environment with a 5% sodium chloride solution at a controlled temperature. It speeds up the corrosion but does not produce real-world environmental fluctuations, so it is best for rapid comparative testing.
In contrast, the Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) applies a multi-cycle test procedure, subjecting samples to cycles of salt spray, humidity, drying, and temperature fluctuation. This mimics more natural weathering conditions, giving a representative assessment of long-term corrosion resistance and coating performance in real-world use.
Salt Spray Test and Cyclic Corrosion Test Standards
Salt spray and Cyclic corrosion tests are conducted in accordance with published standards by organizations such as ASTM International, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and industry-specific organizations.
-
ASTM B117: Standard practice for operating salt spray (fog) apparatus.
-
ISO 9227: Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres – salt spray tests.
-
ASTM G85: Standard practice for modified salt spray (fog) testing, such as cyclic conditions.
-
JIS Z 2371: Japanese standard for salt spray testing.
-
ISO 11997: Paints and varnishes – Determination of resistance to cyclic corrosion conditions.
-
IEC 60068-2-52: Environmental testing – Salt mist, cyclic (corrosion test) for electronic and electrical equipment.
Testronix Instrument: The Best Manufacturer for SST and CCT Test Equipment
Testronix Instruments, a leading manufacturer with decades of experience, provides reliable corrosion testing equipment. Our Salt Spray Chambers (SSC) and Cyclic Corrosion Chambers (CCC) are designed to meet international standards, delivering precise and accurate testing solutions.
Whether you are undertaking fast salt spray tests for quality inspection or cyclic corrosion tests for actual application performance testing, Testronix Instruments offers the most reliable solutions to fit your needs.
Why Prefer Testronix Instruments?
-
Advanced Technology: Integrated with programmable controllers for precise and repeatable tests.
-
Compliance with Standards: Instruments manufactured according to ASTM, ISO, SAE, and VDA standards.
-
Long Lasting Construction: All equipment is constructed using corrosion-proof material to give long-lasting service life.
-
Easy to Operate Interface: Simple operation through digital controls and monitoring capabilities.
-
Flexibility: Applicable across various industries such as automotive, paints & coatings, metal finishing, and research laboratories.
-
Post-Sales Support: Extensive training, calibration, and technical support.
Salt Spray Test (SST) and Cyclic Corrosion Test (CCT) are essential tools in the fight against corrosion. Although SST is inexpensive, quick, and perfect for routine quality inspection, CCT produces very realistic outcomes for companies where safety and long-term reliability are paramount.
The appropriate test method to be used is dependent on the application, the needed accuracy, and industry practices. With state-of-the-art instruments from Testronix Instruments, the producers can guarantee that their products are of the highest corrosion resistance and durable performance.





