The physical properties of materials such as plastics and paper are important to factories and companies where appearance, documentation, protection, and presentation of products are essential. Opacity is affected by how much light can go through each material's coating. For example, when an author creates a high-quality printed book, plastic packaging films are used, and the opacity of the material determines how much light can enter the product.
The proper interpretation and measurement of the degree of opacities allow manufacturers to be consistent, to measure up to standards, and to assure the quality of products. This paper defines the idea of opacity, its significance, mathematical expression and the specific procedures of determining the same in paper and plastics, and the use of a transparency meter.
What is Opacity? Meaning & Uses
Opacity is defined as the extent to which light can pass through a substance, indicating how transparent (or translucent) it is. When it comes to digital design, digital art, and computer graphics, an object can be said to have a certain level of opacity. The term indicates the amount of visibility it provides when placed on top of another item, such as a layer, image, or any type of graphic.
In a nutshell, opacity is an essential quality of paper for use in writing and printing applications. It prevents images or text printed on one side of the paper from being visible on the other side. Opacity is thus crucial in the production of documents such as books, notebooks, legal documents, and packaging. Plastic products also require opacity for a wide range of applications, including packaging, automotive parts, consumer products, medical devices, and films.
Formula to Calculate Opacity of Paper and Plastics
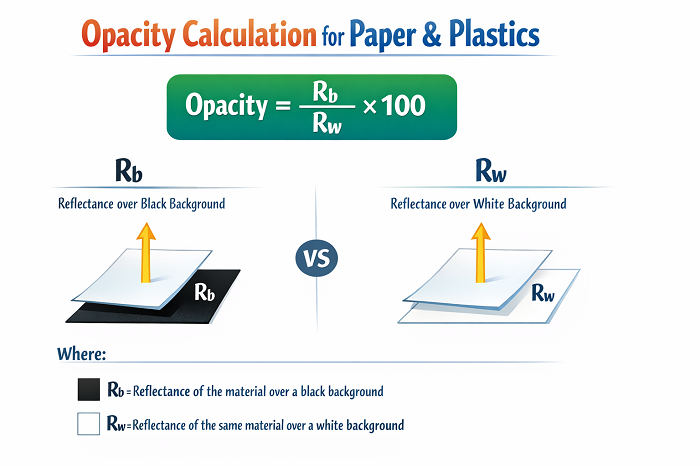
The standard formula for calculating the percentage opacity of materials like paper and plastics is:
Opacity = (R_b / R_w) * 100
Where:
R_b = Reflectance of the material over a black background
R_w = Reflectance of the same material over a white background
How to Measure the Opacity of Paper

To measure the Opacity of paper, a specialized opacity meter is typically utilized. This measuring device evaluates the amount of reflected light from a sample sheet of paper when positioned against two different backgrounds, black and white.
Step by Step using an Opacity Meter: -
-
Calibrate: Calibrate the instrument with reference to white and black.
-
Measure on Black: Place a non-reflective black background under the paper sample and measure the reflectance (R_Black).
-
Measure on White: Place the same sample in the produced sheet of the white paper which is effectively a pad of identical color.
-
Measure the Reflectance (R_white).
-
Calculate: Opacity = (R_black / R_white) * 100. (Some instruments calculate this by default.)
How to Measure the Opacity of Plastics
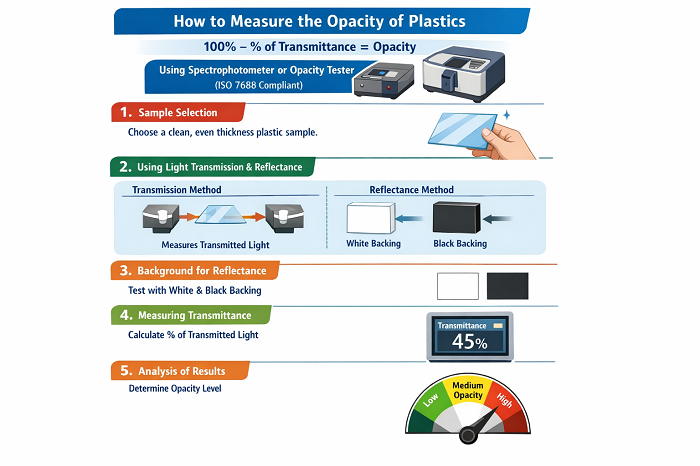
A Spectrophotometer or Opacity Tester can be used to measure the opacity of plastic by shining a beam of light through it, measuring the amount of light that passes through, and then calculating the opacity as follows: 100% - (% of Transmittance). Both of these instruments must conform to ISO 7686 for accuracy.
Step by Step to measure the Opacity of Plastics:-
-
Sample Selection: To clean the sample surface, the surface must be cleaned to eliminate dust, finger prints or any scratches, which can interfere with the functioning of the sample since it will be interfering with the movement of the light through the materials.
-
Using Light Transmission and Reflectance: The opacity of plastic can be measured using reflectance (for plastics that are similar to paper) or by measuring light that has passed through the sample, depending on the type of plastic being tested.
-
Background for Reflectance Method: For testing, reflectance will be measured using white and black backing (that is, the same as with paper).
-
Transmission Method: For transparent and translucent plastic samples, the percentage of transmitted light is measured. The lower the percentage of transmitted light, the greater the level of opacity.
-
Analysis of Results: The final rating of opacity can help determine if the plastic meets the needs of a specific application.
Transparency Meter: A Testronix Instrument to Measure the Opacity
A transparency meter is a specialized instrument used to measure the transparency, translucency, or opacity of materials such as paper, plastic films, paper sheets, and packaging materials. Our Transparency Meters are designed for accurate, consistent, and user-friendly testing in both laboratory and industrial settings.
The Testronix Instruments TX-TR100 Transparency Meter is a precise instrument for measuring the amount of transmitted and blocked light from transparent and opaque materials used in quality control applications.
Conclusion
Opacity is often expressed as a percentage—100% means no light passes through. In industries like paint or paper, it's measured by comparing how the material looks over black vs. white backgrounds. For smoke or emissions, devices check how much light is absorbed or scattered. It's a simple way to ensure quality or meet environmental rules.
The transparency meter can also measure the level of transparency or opaqueness of materials like PET bottles, films, paper and coatings based on the amount of light. The transparency index is between 0 and 100.
To verify the quality of the materials, the transparency meter assists manufacturers in determining the extent of light that is able to penetrate an object or film. It identifies the problems with it and ensures the product looks and functions appropriately even before it is shipped.





