In laboratory and industrial settings contamination from airborne particles can harm research accuracy and the quality of the product. Issues like clogged filters and airflow disturbances can affect its performance. However, regular maintenance, proper usage, and strict hygiene measures ensure its continued reliability.
A Laminar Air Flow Chamber provides a contaminated-free environment by using filtered air to flow evenly and remove contaminants. But what is a Laminar Air Flow hood or chamber? This article will explore the working principle, components, types, and applications of Laminar air flow cabinets in various industries.
What is Laminar Air Flow Hood?
A laminar airflow hood is a laboratory cabinet that provides a continuous, HEPA?filtered, unidirectional airflow to maintain a sterile work zone and protect samples from airborne contamination. When experimenting with a substance, this laboratory equipment protects the samples from air contamination. Laminar airflow will significantly reduce contamination within the workspace by maintaining controlled workspace conditions that are necessary for processes requiring clean and sterile environments.
Why Laminar Air Flow Hood Used?
The Laminar Air Flow Hood is designed to provide a work environment for manufacturers in which the product (culture, pharmacy, or electronic component) is protected from contamination. This is done by providing a continuous supply of filtered air, free of particles, in a clean room and by shielding the product from air movement due to drafts.
Primary reasons and uses for laminar air flow hoods:
-
Contamination Control: The LAF hood separates the contaminating materials of the area and the workspace. It gives the area a working space that is free of particulates to carry out delicate work.
-
Aseptic techniques: Procedures like microbiology, tissue culture, and preparation of media demand an aseptic technique where the need to keep them sterile occurs.
-
Pharmaceutical Compounding: An LAF hood can be applied to offer a safe and dependable procedure for producing medicines that are not deemed to be dangerous to either the employee or the patient.
-
Sensitive Assembly: The LAF hood protects sensitive items that require protection from dust, such as products in the electronics, optics, and semiconductor industries.
-
Sample Protection: The unidirectional airflow (horizontal or vertical) through the LAF hood prevents particles from re-contaminating the work area while performing work.
Laminar Air Flow Hood Diagram Explanation
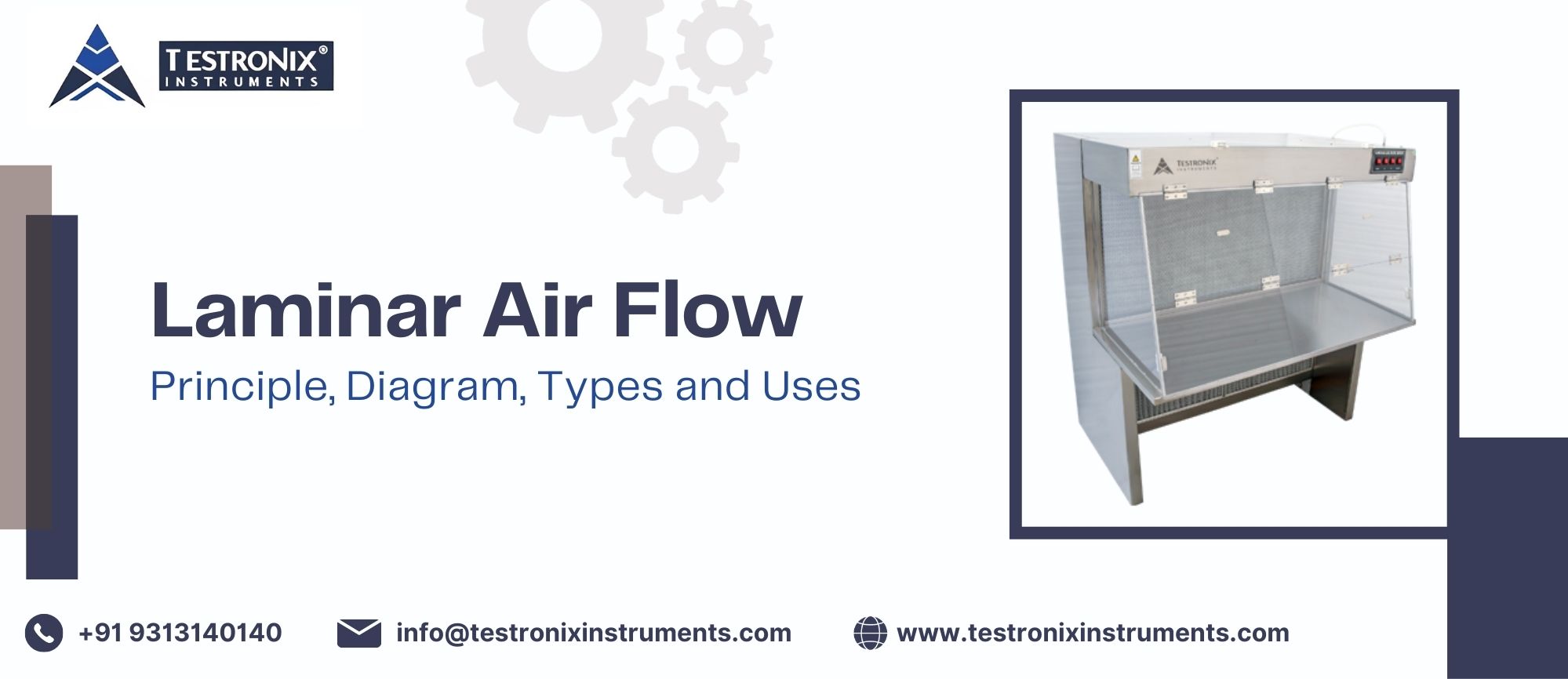
A laminar airflow cabinet diagram consists of various components such as a pre-filter, blower, HEPA filter, working surface, UV and Fluorescent lights, side panels, control panels, and airflow direction to ensure a contaminated-free environment. The following are the key parts of laminar air flow hood diagram –
-
Cabinet/Work Surface: This is usually made of stainless steel (mostly SUS304) such that it is easy to clean, sterile, and has no leaks, so as to ensure a sterile, leak-proof, and easy-to-work-in environment.
-
Pre-Filter: This unit is installed on the top or rear of a cabinet/work surface to trap the coarse particles that may be carried to the air, and this may reduce the life of the main filter.
-
Blower/Fan: The air flow required is made by the blower, which then pulls the ambient air into the cabinet via the filters.
-
HEPA Filter: It is the most significant component of the filter system because it eliminates 99.97 percent of all the particles in the air, and it removes bacteria and fungi as well as dust that is larger than 0.3 m in size.
-
Diffuser Screen: This is located behind the HEPA filter and gives an even velocity and smooth movement of gas within the workspace.
-
UV Lamp: Installed to disinfect the work surfaces after use.
-
Fluorescent Light: Provides light to perform work in the workspace.
-
Front Sash (Glass Shield): This is a moving, see-through barrier that protects the worker from the laminar airflow containing potentially harmful particulate matter, as well as protecting the material being worked on from exposure to external ambient air.
Types of Laminar Air Flow Hood
The two primary types of laminar air flow hoods are Horizontal and Vertical laminar flow hoods. These are defined by the direction of airflow and the filter position.
-
Vertical Laminar Flow Cabinet
Vertical flow cabinets have air movement from top to bottom. The amount of depth and floor space required for a working bench with vertical airflow is less than that of a horizontal airflow hood. This makes it easier to manage and less likely to obstruct airflow or move contaminated air upstream.
-
Horizontal Laminar Flow Cabinet
In horizontal-flow laminar flow cabinets, air enters from the rear (back) of the workstation and is forced by a blower towards HEPA filters. The resulting filtered air is then expelled horizontally towards the work area. One of the benefits of this type of cabinet is the fact that clean air is continually moving parallel to the work site at a constant speed to maintain a cleansed environment.
Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Flow Hoods
Horizontal and Vertical Laminar Flow Hoods keep the workspace clean but have different airflow directions. Horizontal hoods blow air from behind the work area, while vertical hoods push air from above. Vertical hoods protect the user more, while horizontal hoods cause less airflow disturbance near samples.
|
Feature |
Horizontal Flow Cabinet |
Vertical Flow Cabinet |
|
Airflow Direction |
Back to front |
Top to bottom |
|
Contamination Risk |
Lower user interference |
Reduced risk from hand movement |
|
Space Requirement |
Requires more depth |
Suitable for compact spaces |
|
Operator Safety |
Less protective against hazardous materials |
Better protection from hazardous fumes |
Laminar Air Flow Hood Principle
The laminar air flow hood principle is based on unidirectional, filtered airflow. Air enters the cabinet by passing through an air filter, which removes dirt and dust before being forced by a fan through the HEPA filter. The resulting air is free of contamination. The clean airflow from the HEPA filter flows evenly across the work surface of the cabinet, providing a positive pressure under the work surface to keep any bacteria or dust from entering the cabinet.
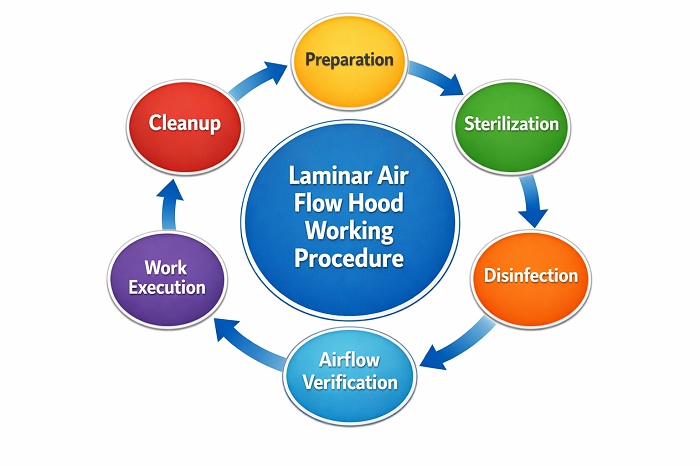
Laminar Air Flow Hood Working Procedure
A laminar air flow working procedure is based on several steps, such as preparation, sterilization, disinfection, airflow verification, work execution, and cleanup.
Here are the major steps described:
Preparation
Before commencing any tasks, the blower and light switches are on for a minimum of 15–30 minutes. This enables HEPA-filtered air to flow around inside the cabinet, removing contaminants from the air and creating stable laminar flow.
Sterilization
The first step in sterilizing the cabinet is to use UV light to destroy microorganisms on its internal surfaces. The UV lights need to be turned on for approximately 15–20 minutes before the start of work and then turned off, as the risk of skin and eye damage will occur if exposed to UV light after completion of work.
Disinfection
To maintain a clean and sterile environment, it begins by wiping the working surface of stainless steel with 70 percent isopropyl alcohol (or other permitted disinfectant). This is a disinfection process that eliminates not only surface contaminants but also any other microbial growth that may have been caused by previous users. Hence, create a clean environment before you introduce your materials and equipment into the cabinet.
Airflow Verification
Open sash/glass panels to the recommended operating height for proper airflow velocity; this will provide effective laminar flow (keeping external air pollutants from contaminating your work), protecting your sample(s) from contamination by outside sources, and also protecting yourself.
Work Execution
While working, slow, intentional movement should limit the disruption of laminar air flow. All materials will be kept within 3–6 inches of the hood, and all air vents will remain free of obstructions to promote even air flow and control contamination.
Cleanup
The procedure would be followed by washing the work surface again with disinfectant to eliminate any residues or contamination on the work surface. After cleaning the work surface, the lights and blower will be switched off. Hence, the next user of the cabinet will have a clean and safe one.
Applications of Laminar Air Flow Hood
Laminar air flow hoods are helpful in several applications such as microbiology & bacteriology, pharmaceutical industries, plant tissue culture (biotech), electronics & semiconductor manufacturing, and medical & clinical labs.
Here are the applications described in detail:
-
Microbiology & Bacteriology
A laminar air flow cabinet is a vital technique for safe handling, transferring, cultivating, and one-way culturing of bacteria, fungi, and viruses in microbiological and bacteriological labs. This cabinet also provides a sterilized environment that reduces airborne pollution and ensures reliable results in laboratory tests.
-
Pharmaceutical Industries
The pharmaceutical sector is a highly active industry that utilizes laminar airflow cabinets during aseptic processing. They are applied in the production of sterile pharmaceuticals like sterile drugs, intravenous solutions, and vaccines, among other pharmaceuticals, and guarantee that contamination and product safety are upheld.
-
Plant Tissue Culture (Biotech)
Laminar flow cabinets are needed in biotechnology as well as plant tissue culture, as they must carry out aseptic processing of plant cells, tissues, and explants. This permits multiplication-free environments which are essential in the initiation of plant cultures and also in sustaining their growth by regeneration.
-
Electronics & Semiconductor Manufacturing
On the other hand, the electronics and semiconductor industries are also requiring the laminar flow cabinets to enclose the microprocessors and other electronic parts and nanomaterials during the production process. As such, in order to make sure that these materials do not interfere with the quality, precision, and reliability of their products, it is necessary to supply controlled and clean air around these materials in order to accommodate assembly and fabrication.
-
Medical & Clinical Labs
IVF clinic laminar airflow cabinets are of great necessity to offer sterile conditions to culture fragile embryos. Pathology laboratories also use laminar air flow cabinets to safely work with reduced chances of contamination in samples to keep the reliability and accuracy of the diagnostic tests.
Conclusion
A laminar air flow hood is a necessary laboratory equipment item, which keeps the laboratory environment clean and free. A laminar air flow hood is essential in microbiology, pharmacy, and research laboratories, as it is maintained by introducing HEPA-filtered air with the help of laminar flow technology. Therefore, it guarantees that experiments are of high levels of accuracy, safety, and reliability.