Reviewed by Anurag Mishra (Sr. Technical Consultant)

In the field of material testing, understanding how materials respond to stress is crucial for guaranteeing their unwavering quality and well-being in true applications. A significant test to serve this purpose is the Charpy Impact Test. This is the mechanical assessment used to determine rigid plastics' toughness and impact strength. This test is done using a Charpy Impact Testing Machine, adhering to the standards given by ASTM D6110 and other similar standards. From the rigid plastic family, polycarbonate, acrylic, ABS, and polypropylene are considered suitable for this test, mainly because of their structural features.
This blog presents the reason why the Charpy Impact Test is so significant along with its key concepts, and provides detailed information on how a Charpy test is conducted along with complete details of how to carry it out.
The Charpy Impact Test is crucial in material science and manufacturing. Its main significance includes:
This Charpy Impact Test is based on several scientific principles very clearly explaining how this test was achieved in terms of the design and working of the testing instrument.
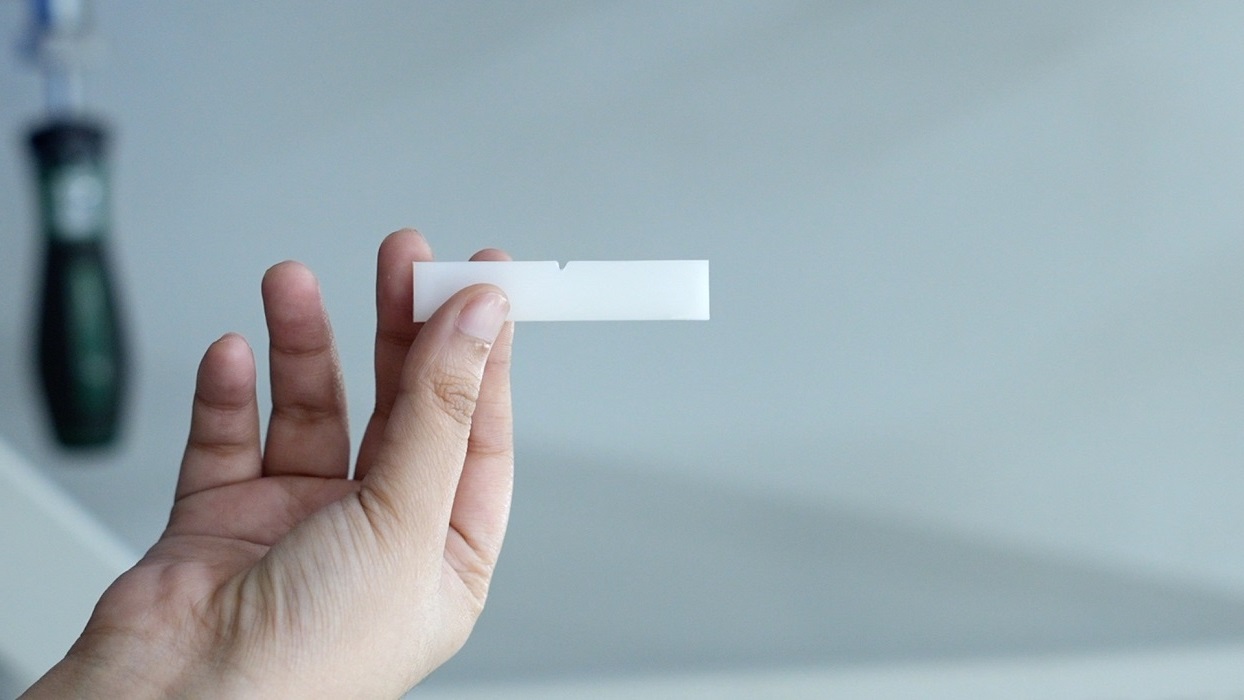
The test requires specimens with standardized dimensions of 127 mm in length, 12.7 mm in width, and up to 3 mm in thickness.
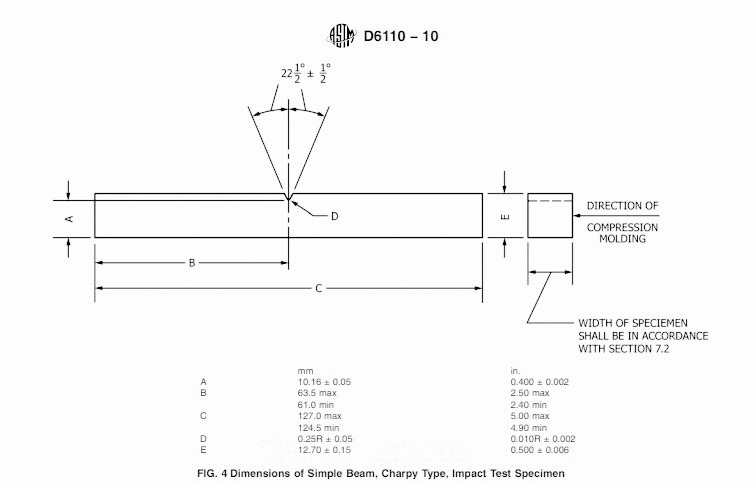
A V-notch or U-notch is machined at the centre of the specimen, with a radius of 0.25 R mm to ensure stress concentration for accurate breakage.
The notch is created using specialized tools to guarantee precision. It is located in the middle of the specimen to allow for uniform energy absorption during impact.
Notch depth in plastic samples. It insists that the leftover depth of plastic material at which the notch is imposed should be in the range of 10.16 ± 0.05mm (0.400 ± 0.002 in). The same measurement should be done employing an apparatus. The tapered blade that is used in the notch Anvil should provide vertical support in between the test specimen.
The standard requires a notch because it simplifies the pendulum's task of breaking the material, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
The specimen is held horizontally on a testing fixture adapted for the Charpy Impact Test, which varies from the test fixture used with the Izod Test. The positioning of the specimen should be standardized to ensure direct striking by the pendulum at the notch.
FIXTURE USED IN CHARPY TEST

The weight put on the pendulum is adjusted based on the material being tested. With five weight options available, the machine is versatile for various plastics.
WEIGHTS FOR PENDULUM

Calibration is performed for low or high-capacity testing based on the toughness of the material.
The pendulum is released to strike the specimen at the notched point. The energy taken in during the impact is measured, showing the toughness of the material.
The machine’s transducer changes the absorbed energy into an electrical signal for accurate data collection.
The Charpy Impact Test offers several advantages that make it a vital method in material testing. Compliance with ASTM D256 guarantees consistent and dependable results. It is applicable to a broad spectrum of rigid plastics. The use of digital models improves precision through automated calculations and reporting. Additionally, adaptable weight configurations allow for the testing of various materials.
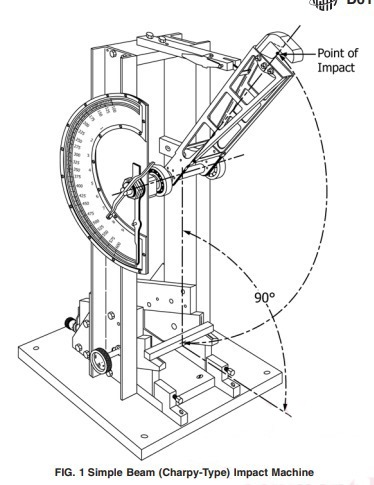 WORKING MECHANISM OF CHARPY IMPACT TEST
WORKING MECHANISM OF CHARPY IMPACT TEST
AS PER STANDARD D6110
FAQs
A notch is crucial as it focuses stress at a designated point, which ensures uniform and accurate breakage during the test. This is essential for assessing the material's actual impact resistance.
Yes, the test is also applicable to both thermoplastics and thermosets like phenolic resin.
The digital model includes features like transducers for energy conversion, automated data logging, and an instant display of impact energy and angle of inclination, all of which contribute to precise measurements and efficient reporting.
Ensure your materials meet industry standards with our advanced Charpy Impact Tester. Whether for quality control or R&D, we’ve got you covered.